Diseases in the Shoulder Joint Area②
Management of pain caused by a combination of inflammation and contracture

Differences between the symptoms of rotator cuff tear and frozen shoulder
Both conditions present with similar complaints of shoulder pain and limited movement. They also commonly include nighttime shoulder aching. However, careful observation reveals distinct differences. Below, the symptoms of typical rotator cuff tear cases and those with frozen shoulder–like symptoms are presented.
How to proceed with the examination
Differences in examination findings between two patients
Elderly man
・ Shows pain beyond a certain range during passive movement, but overall range of motion is relatively good
・ Experiences pain during hand-to-back (belt) movement and shoulder elevation
・ Feels pain when lowering the arm
・ Pain is relieved after injection, but muscle strength remains weak
Younger man
・ Experiences pain in various directions, and there is a limitation of range of motion even during passive movement
・ Abduction is difficult
The elderly man was diagnosed with a rotator cuff tear.
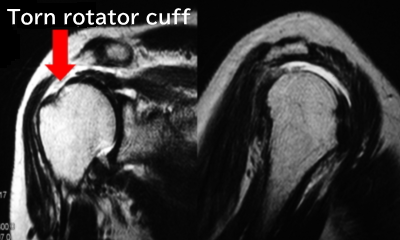
The younger patient
Pathologically, ongoing inflammation leads to contracture caused by decreased extensibility of the rotator cuff muscles, and physical therapy is the first-line treatment.
Differences between contracture and rotator cuff tear
Contracture
- Range of motion limitation is observed during passive movement
- Resistance felt at the end range of passive motion
- Pain and range of motion limitation in multiple directions
Rotator cuff tear
- Passive movement is relatively good
- Pain and catching sensation in specific positions
- Not present in multiple directions
Treatment for rotator cuff tear: Indication for surgery!
- Subacromial impingement
Patients who have pain and catching sensations and wish for a definitive cure. - Muscle weakness and loss of strength
When rotator cuff function is impaired, weakness often cannot be fully resolved without surgery, and patients seek a definitive cure. - When contracture associated with rotator cuff tear is resistant to conservative treatment
Indications for surgery in rotator cuff tear
Pattern ①
A relatively small tear with catching as the main symptom.
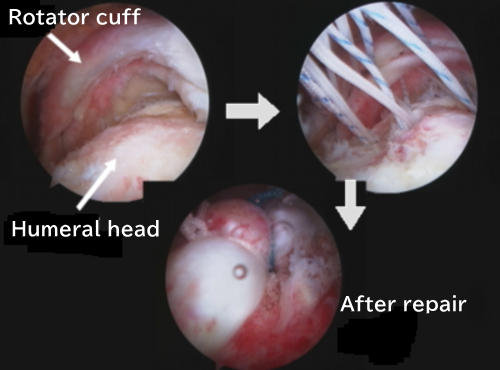
In surgery:
- Remove the catching!
- Perform acromioplasty
- Repair the rotator cuff
Pattern ②
Cannot maintain the centered position (optimal joint position).
Symptoms include muscle weakness, loss of strength, and persistent catching sensation.
- Restore the centered position without catching
- Rotator cuff repair (reconstruction of rotator cuff function)
Pattern ③
Rotator cuff tear complicated by contracture
- Symptoms include persistent muscle weakness, loss of strength, and catching sensation.
- Large tears following trauma
Severe scar formation is common, and the rotator cuff often adheres to the acromion and bursa.
2.Progression from impingement due to partial tear
When the bursa is torn, persistent catching between the acromion and bursa can lead to severe bursitis, and prolonged course may result in contracture.
・ Relatively small tear causing catching
- Partial or complete tear on the bursal side
・ Larger tear with inability to maintain the centered position
- Weakness or subacromial impingement
・ Cases complicated by moderate contracture
- Associated with complete rotator cuff tear
- Associated with traumatic large rotator cuff tear
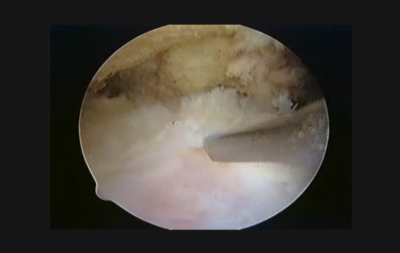
When viewing an intact rotator cuff from the bursal side with an arthroscope
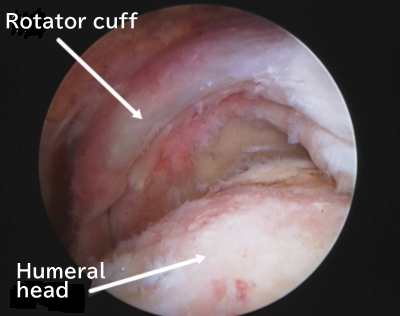
When viewing a torn rotator cuff with an arthroscope
Arthroscopic surgery
Examination Process

Medical Interview → Physical Examination (Assessment of symptoms such as pain when moving the shoulder) → Management of Inflammation → Prescription of Physical Therapy → MRI and other tests → Surgery.
